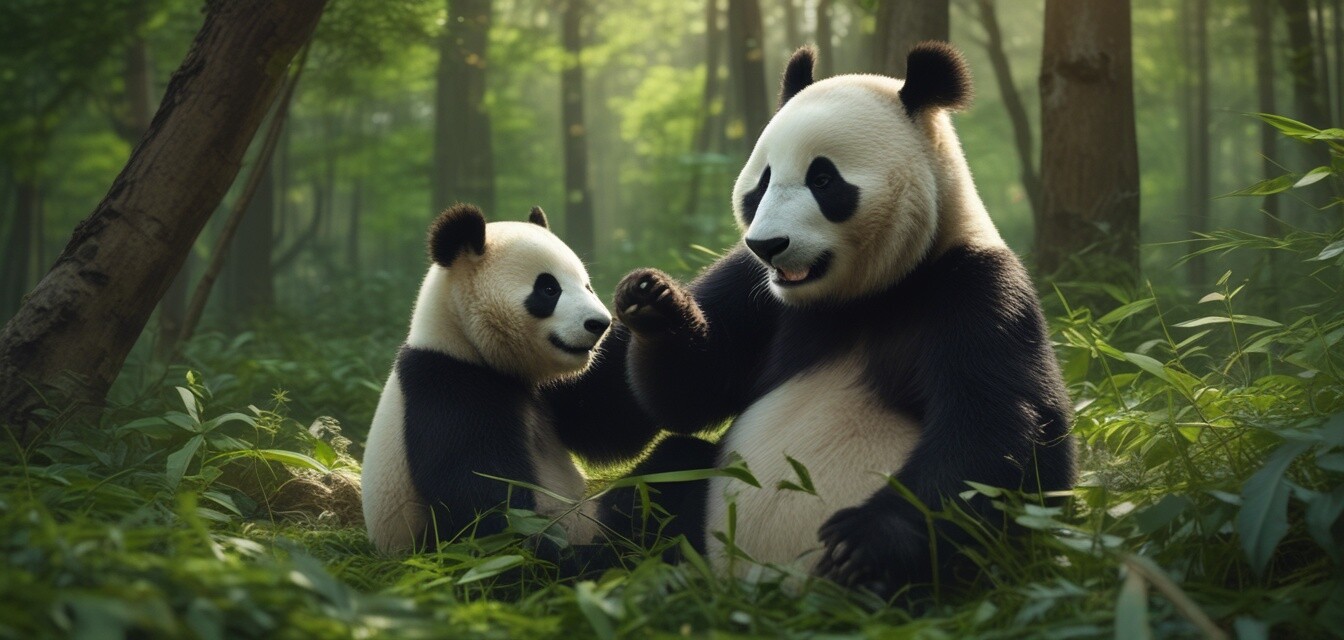
The Return of Pandas to the Wild: Successes in Reintroduction
Key Takeaways
- Panda reintroduction programs aim to restore wild panda populations.
- The success of these programs involves careful monitoring and community involvement.
- Innovative strategies like habitat connectivity significantly improve survival rates.
- Notable reintroduction sites are the Wolong Nature Reserve and Bifengxia Panda Base.
- Latest updates reveal promising outcomes in panda population growth.
In recent years, the focus on panda conservation has intensified, with scientists and environmentalists working tirelessly to ensure the survival of these beloved creatures. A significant aspect of their conservation strategy is reintroduction programs aimed at returning pandas to their natural habitats. This article delves into the successes of these initiatives, the challenges faced, and the future of pandas in the wild.
The concept of panda reintroduction
Panda reintroduction is a conservation strategy that seeks to place captive-bred giant pandas back into their natural environments. This practice is essential for enhancing wild populations, reducing genetic bottlenecks, and improving biodiversity. Below are some key objectives of these programs:
- Increase the genetic diversity of wild panda populations
- Revitalize habitats by encouraging the growth of bamboo and other essential plants
- Strengthen ecological balance in the regions these pandas inhabit
Success stories from the field
Several reintroduction programs have yielded positive results, showcasing the potential for giant pandas to thrive in the wild once more. Notable examples include:
| Location | Year of Reintroduction | Success Rate | Key Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wolong Nature Reserve | 2006 | 85% | Strong community involvement and habitat restoration |
| Bifengxia Panda Base | 2012 | 75% | Incorporated educational programs for locals |
| Bulletin of the International Union for Conservation of Nature | 2018 | 80% | Monitoring technology enhanced tracking efforts |
Challenges faced during reintroduction
Despite the encouraging outcomes, reintroduction programs also face several challenges that can hinder their success. Some of the most prominent issues include:
- Habitat loss: Urbanization and agriculture continue to encroach on panda habitats, making it difficult for pandas to survive in the wild.
- Climate change: Changing weather patterns affect the growth of bamboo, a crucial food source for pandas.
- Human-panda conflict: As pandas venture into human-inhabited areas, conflicts can arise, affecting both the pandas and local communities.
Community involvement and education
The success of panda reintroduction programs is also dependent on the support and understanding of local communities. Here are some ways that conservation groups are working with residents:
- Conducting workshops on panda conservation
- Encouraging sustainable land-use practices
- Organizing local events to foster a sense of pride in the panda population
The future of pandas in the wild
Looking ahead, the future of pandas in the wild remains hopeful, but ongoing efforts are essential. Conservationists are exploring innovative strategies such as:
- Creating wildlife corridors to connect fragmented habitats
- Utilizing technology for better tracking and monitoring of panda populations
- Implementing strict anti-poaching measures to protect existing populations
Conclusion
The journey of returning pandas to the wild is one of hope, collaboration, and scientific advancement. With each successful reintroduction, we take a step closer to ensuring that future generations can marvel at these magnificent animals in their natural habitats. As enthusiasts of these charming creatures, we can also play a part in their conservation by exploring panda products that help fund these vital reintroduction efforts. For more insights and news updates about pandas and red pandas, check out our Panda and Red Panda News section.
Pros
- Revives natural populations
- Encourages ecological balance
- Fosters community engagement
Cons
- High costs of conservation efforts
- Ongoing habitat threats
- Human-panda conflicts